An ice-free Arctic in just 23 years?
Big fucking surprise. Or not. Look… how many times do we have to see these words over and over? “Sooner than expected”, “much worse than previously thought”. I’ve said it before, this is happening at a pace far faster than even the worst predictions. We have got to start thinking of climate change as RIGHT FUCKING NOW. This is NOW. This is not 100 years from now. This is not great grand children or the next generation. FUCK. Stop eating meat. Stop driving. Stop consuming. FUCKING STOP.
I hate humanity and truthfully, I think I’m starting to take pleasure in seeing people suffer from weather related catastrophes. If only that suffering were more focused on the U.S. and other primary contributors of atmospheric carbon. It’s harsh I know but FUCK. How stupid, shortsighted and selfish can we be?
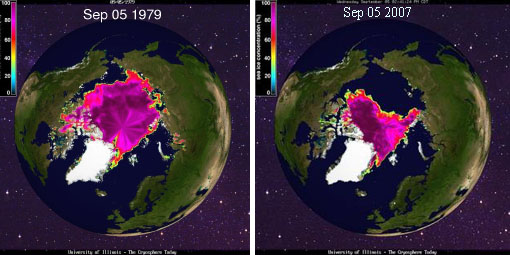
Comparison of sea ice area on September 5, 1979 and September 5, 2007.
Sea ice area in early September has declined 42% in the 28 years since 1979.
Image credit: University of Illinois Polar Research Group.
Jeff Masters over at Wunderground discusses the issue:
None of our computer climate models predicted that such a huge loss in Arctic ice would occur so soon. Up until this year, the prevailing view among climate scientists was that an ice-free Arctic ocean would occur in the 2070-2100 time frame. The official word on climate change, the February 2007 report from the U.N.-sponsored Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), warned that without drastic changes in greenhouse gas emissions, Arctic sea ice will “almost entirely” disappear by the end of the century. This projection is now being radically revised. Earlier this year, I blogged about a new study that predicted abrupt losses of Arctic sea ice were possible as early as 2015, and that we could see an ice-free Arctic Ocean as early as 2040. Well, the Arctic Ocean has suffered one of the abrupt losses this study warned about–eight years earlier than this most radical study suggested. It is highly probable that a complete loss of summer Arctic sea ice will occur far earlier than any scientist or computer model predicted. In an interview published yesterday in The Guardian Dr. Mark Serreze, and Arctic ice expert with the National Snow and Ice Data Center, said: “If you asked me a couple of years ago when the Arctic could lose all of its ice, then I would have said 2100, or 2070 maybe. But now I think that 2030 is a reasonable estimate. It seems that the Arctic is going to be a very different place within our lifetimes, and certainly within our children’s lifetimes.” While natural fluctuations in wind and ocean circulation are partly to blame for this loss of sea ice, human-caused global warming is primarily to blame. In the words of Dr. Serreze: “The rules are starting to change and what’s changing the rules is the input of greenhouse gases. This year puts the exclamation mark on a series of record lows that tell us something is happening."
The implications
The melting of the Arctic sea ice will not raise ocean levels appreciably, since the ice is made up of frozen sea water that is floating in the ocean. Sea ice melt does contribute slightly to sea level rise, since the fresh melt water is less dense than the salty ocean water it displaces. According to Robert Grumbine’s sea level FAQ, if all the world’s sea ice melted, it would contribute to about 4 millimeters of global sea level rise. This is a tiny figure compared to the 20 feet of sea level rise locked up in the ice of the Greenland ice sheet, which is on land.
The biggest concern about Arctic sea ice loss is the warmer average temperatures it will bring to the Arctic in coming years. Instead of white, reflective ice, we will now have dark, sunlight-absorbing water at the pole, leading to a large increase in average temperature. Warmer temperatures will accelerate the melting of the Greenland ice sheet, which holds enough water to raise sea level 20 feet. The official word on climate, the 2007 IPCC report, predicted only a 0.6-1.9 foot sea level rise by 2100, due to melting of the Greenland ice sheet and other factors. I believe these estimates will need to be revised sharply upwards in light of the unexpectedly high Arctic sea ice loss this summer.
One more point–global warming skeptics often criticize using computer model climate predictions as a basis for policy decisions. These models are too uncertain, they say. Well, the uncertainty goes both way–sometimes the models will underestimate climate change. We should have learned this lesson when the ozone hole opened up–another case where the models failed to predict a major climate change. The atmosphere is not the well-behaved, predictable entity the models try to approximate it as. The atmosphere is wild, chaotic, incredibly complex, and prone to sudden unexpected shifts. By pumping large amounts of greenhouse gases into the air, we have destabilized the climate and pushed the atmosphere into a new state it has never been in before. We can expect many more surprises that the models will not predict. Some of these may be pleasant surprises, but I am expecting mostly nasty surprises.